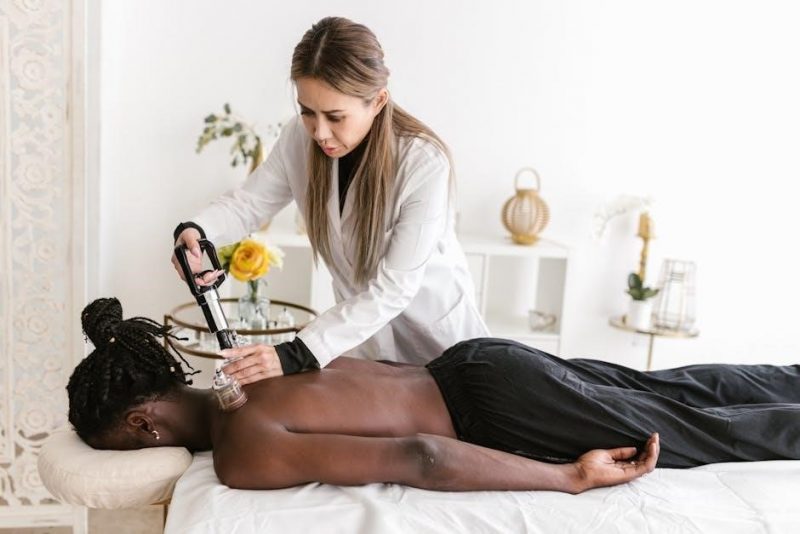
integrated manual therapist
Discover expert techniques for pain relief and wellness through integrated manual therapy. Proven methods for a healthier you. Start your journey today!
Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) is a comprehensive‚ evidence-based approach combining soft tissue mobilization‚ joint manipulation‚ and neuromuscular techniques to restore function and relieve pain. It emphasizes a holistic‚ patient-centered model‚ addressing the entire body to promote healing and optimal movement.
By integrating various manual therapies‚ IMT offers personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs‚ fostering long-term recovery and wellness.
1.1 Definition and Overview
Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) is a comprehensive‚ evidence-based approach that combines various manual techniques to address soft tissue‚ joint‚ and neuromuscular dysfunction. It is a patient-centered modality designed to restore optimal movement‚ reduce pain‚ and enhance overall bodily function. By integrating diverse therapeutic methods‚ IMT provides a holistic treatment model that targets the root causes of dysfunction‚ promoting long-term recovery and wellness. This approach is tailored to individual needs‚ ensuring personalized care and effective outcomes.
1.2 Historical Background
The origins of Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) trace back to ancient practices of manual healing‚ including massage and joint manipulations. Early civilizations‚ such as Egyptian‚ Chinese‚ and Greek cultures‚ used hands-on techniques to treat injuries and ailments. In the 19th and 20th centuries‚ osteopathy and chiropractic care emerged‚ laying the foundation for modern manual therapies. The mid-20th century saw the development of techniques like myofascial release and trigger point therapy‚ further expanding the scope of manual interventions. These traditions merged to form IMT‚ a holistic approach emphasizing evidence-based‚ patient-centered care.
1.3 Key Principles and Objectives
Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) is grounded in evidence-based practices‚ focusing on a patient-centered approach to restore optimal function and well-being. Its core principles include addressing the interconnectedness of the body’s systems‚ promoting natural healing processes‚ and tailoring treatments to individual needs. The primary objectives are to enhance mobility‚ reduce pain‚ and improve overall physical and emotional health. By combining diverse manual techniques‚ IMT aims to create a balanced and sustainable approach to recovery‚ empowering patients to achieve long-term wellness and independence.

Role and Responsibilities of an Integrated Manual Therapist
An Integrated Manual Therapist assesses patients‚ diagnoses issues‚ and applies hands-on techniques to restore function and alleviate pain. They collaborate with healthcare professionals to create personalized treatment plans‚ ensuring holistic care and optimal recovery outcomes.
2.1 Patient Assessment and Diagnosis
An Integrated Manual Therapist begins with a thorough patient assessment‚ including a detailed medical history and physical examination. They use techniques like palpation and range-of-motion tests to identify soft tissue and joint imbalances. The therapist analyzes posture‚ movement patterns‚ and pain triggers to diagnose underlying issues. This process ensures personalized treatment plans addressing the root cause of dysfunction. Collaboration with other healthcare professionals may occur to confirm diagnoses‚ ensuring a comprehensive approach to care and optimal patient outcomes. This step is crucial for effective therapy.
2.2 Treatment Techniques and Modalities
Integrated Manual Therapists employ a variety of hands-on techniques to address pain‚ dysfunction‚ and limited mobility. Soft tissue mobilization‚ joint manipulation‚ and myofascial release are commonly used to restore tissue flexibility and joint movement. Neuromuscular techniques may also be applied to improve muscle function and reduce tension. These modalities are often combined to create a personalized treatment plan‚ ensuring a comprehensive approach to patient care. The goal is to enhance mobility‚ reduce pain‚ and promote overall musculoskeletal health through targeted‚ evidence-based interventions.
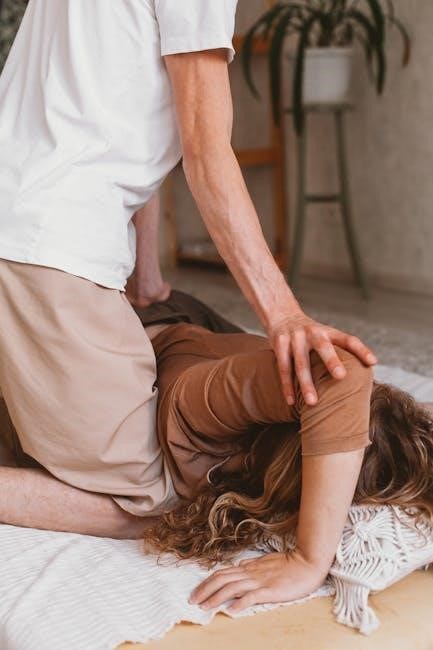

2.3 Collaboration with Other Healthcare Professionals
Integrated Manual Therapists often collaborate with physical therapists‚ chiropractors‚ osteopaths‚ and other healthcare providers to ensure comprehensive patient care. This interdisciplinary approach allows for shared insights and tailored treatment plans‚ addressing the patient’s needs from multiple perspectives. By working together‚ professionals can achieve better outcomes‚ particularly for complex or chronic conditions. Effective communication and teamwork are essential to integrating manual therapy with other therapies‚ ensuring a cohesive and patient-centered approach to healing and recovery. This collaboration enhances the overall quality of care and improves patient satisfaction.
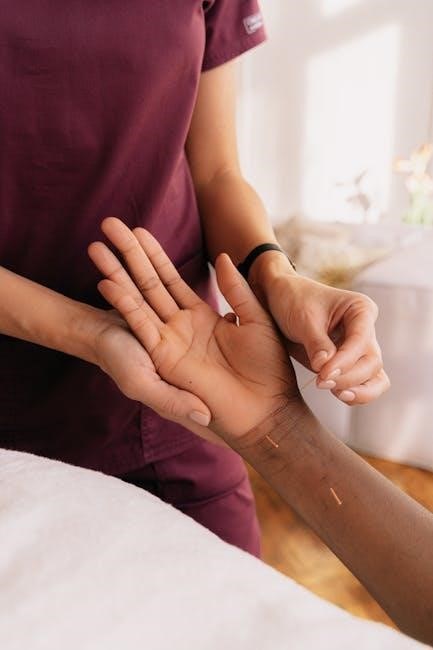

Educational Requirements and Certification
Becoming an Integrated Manual Therapist requires specialized education and certification. Professionals typically undergo comprehensive training in manual therapy techniques‚ anatomy‚ and evidence-based practices. Certification ensures expertise.
3.1 Academic Background and Degrees
An Integrated Manual Therapist typically holds a degree in a healthcare field‚ such as physical therapy‚ occupational therapy‚ or chiropractic care. A Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT) or equivalent is common. Academic programs emphasize anatomy‚ physiology‚ and biomechanics‚ providing a foundation for manual techniques. Many therapists also pursue specialized certifications in integrated manual therapy through accredited programs. These programs often include hands-on training and evidence-based practices to ensure competency in diverse therapeutic methods. A strong academic background ensures a comprehensive understanding of the human body and its functional systems‚ essential for effective treatment.
3.2 Certification Programs and Licensure
Certification in Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) typically requires completion of specialized programs offered by accredited institutions. These programs often include hands-on training‚ theoretical knowledge‚ and clinical practice. Licensure to practice varies by region but generally requires a degree in a related healthcare field and passing certification exams. Many therapists obtain certifications like IMT-C or similar designations‚ demonstrating expertise in manual therapy techniques. Maintaining certification often involves continuing education to stay updated on evidence-based practices and industry standards.
3.3 Continuing Education and Professional Development
Continuing education is essential for integrated manual therapists to stay updated on evidence-based practices and industry advancements. Professional development often involves attending workshops‚ seminars‚ and online courses to refine skills and learn new techniques. Many certification programs require ongoing education credits to maintain licensure. Engagement in professional organizations and peer networking further enhances knowledge sharing and career growth. This commitment ensures therapists provide the most effective‚ current care‚ improving patient outcomes and staying aligned with evolving healthcare standards.

Techniques and Methods Used in Integrated Manual Therapy
Integrated Manual Therapy incorporates techniques like soft tissue mobilization‚ joint manipulation‚ myofascial release‚ and trigger point therapy. These methods aim to restore mobility‚ reduce pain‚ and enhance function.
4.1 Soft Tissue Mobilization
Soft tissue mobilization is a cornerstone technique in Integrated Manual Therapy‚ focusing on muscles‚ tendons‚ and ligaments to relieve tension and pain. This method involves gentle‚ sustained pressure to break adhesions‚ improve circulation‚ and restore normal tissue function. It is often used to address chronic pain‚ inflammation‚ and limited range of motion.
By targeting specific areas of restriction‚ soft tissue mobilization enhances flexibility‚ reduces stiffness‚ and promotes overall musculoskeletal health‚ making it a key component of IMT’s holistic approach to patient care.
4.2 Joint Mobilization and Manipulation
Joint mobilization and manipulation are essential techniques in Integrated Manual Therapy‚ focusing on improving joint mobility and reducing stiffness. Mobilization involves gentle‚ repetitive movements to enhance range of motion‚ while manipulation uses precise thrusts to restore joint function. These methods alleviate pain‚ improve flexibility‚ and address conditions like arthritis or post-injury stiffness.
By targeting joint restrictions‚ therapists can restore normal movement patterns‚ reduce muscle spasms‚ and promote overall joint health‚ making these techniques integral to IMT’s approach to musculoskeletal care.
4.3 Myofascial Release
Myofascial release is a gentle‚ hands-on technique used to relieve tension in the fascia‚ the connective tissue surrounding muscles. By applying sustained pressure‚ therapists release restrictions‚ improving circulation and reducing pain. This method addresses chronic stiffness‚ scar tissue‚ and limited range of motion.
It is often combined with other therapies to enhance recovery‚ making it a cornerstone of Integrated Manual Therapy for restoring soft tissue balance and promoting overall musculoskeletal health.
4.4 Trigger Point Therapy
Trigger Point Therapy focuses on relieving pain and tension by targeting specific areas of muscle tissue known as trigger points. These points are hyperirritable areas that can cause localized or referred pain. Therapists apply sustained pressure to deactivate these points‚ reducing muscle spasms and improving circulation. This technique is particularly effective for chronic pain‚ stiffness‚ and limited mobility.
By addressing these areas‚ Trigger Point Therapy enhances overall muscle function and restores range of motion‚ making it a valuable component of Integrated Manual Therapy.
4.5 Neuromuscular Techniques
Neuromuscular Techniques (NMT) focus on the interaction between the nervous system and soft tissues to restore normal muscle function. This approach addresses imbalances in the musculature caused by injury‚ stress‚ or chronic conditions. By applying gentle‚ sustained pressure to specific areas‚ therapists release tension‚ improve circulation‚ and reduce pain. NMT is particularly effective for conditions like sciatica‚ fibromyalgia‚ and chronic stiffness.
It enhances range of motion and alleviates discomfort‚ making it a key component of Integrated Manual Therapy for long-term recovery and wellness.

Benefits and Applications of Integrated Manual Therapy
Integrated Manual Therapy offers numerous benefits‚ including pain relief‚ improved mobility‚ and enhanced recovery. It addresses chronic conditions‚ promotes relaxation‚ and supports rehabilitation‚ making it versatile for various patient needs.
5.1 Pain Management and Relief
Integrated Manual Therapy excels in pain management by targeting the root causes of discomfort. Techniques like soft tissue mobilization and joint manipulation reduce inflammation‚ relieve muscle tension‚ and restore normal movement patterns. This approach not only alleviates acute and chronic pain but also improves circulation and nervous system function. By addressing both physical and emotional contributors to pain‚ IMT promotes lasting relief and enhances overall well-being‚ helping patients achieve a pain-free lifestyle and improved quality of life.
5.2 Improved Mobility and Flexibility
Integrated Manual Therapy significantly enhances mobility and flexibility by addressing restrictions in soft tissues‚ joints‚ and the nervous system. Techniques like joint mobilization and soft tissue work help break down scar tissue and adhesions‚ restoring natural movement. Improved range of motion reduces stiffness and enables patients to perform daily activities and athletic endeavors with greater ease. This therapy also strengthens posture and balance‚ further promoting long-term flexibility and mobility‚ making it an ideal solution for individuals seeking to maintain an active and healthy lifestyle.
5.3 Rehabilitation and Recovery
Integrated Manual Therapy plays a pivotal role in rehabilitation and recovery by restoring function and strength after injuries or surgeries. Techniques such as joint mobilization and soft tissue work promote tissue repair and reduce inflammation. This therapy also enhances neuromuscular coordination‚ improving balance and stability. By addressing scar tissue and adhesions‚ IMT accelerates recovery‚ enabling patients to return to normal activities faster. Its focus on restoring movement and reducing pain makes it an essential tool in post-injury and post-surgical rehabilitation‚ empowering patients to achieve full recovery and maintain long-term wellness.
5.4 Stress Reduction and Relaxation
Integrated Manual Therapy is highly effective in promoting stress reduction and relaxation by targeting tension in the body. Techniques like myofascial release and soft tissue mobilization help release physical stress stored in muscles and connective tissues. This therapy also stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system‚ encouraging a state of deep relaxation. By addressing chronic tension and improving circulation‚ IMT reduces stress hormones like cortisol‚ enhancing overall well-being. Regular sessions can lead to better sleep‚ emotional balance‚ and a renewed sense of calm‚ making it a valuable tool for managing stress and promoting relaxation in both body and mind.
5.5 Chronic Condition Management
Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) plays a vital role in managing chronic conditions by addressing underlying tissue dysfunction and promoting long-term health. Techniques such as soft tissue mobilization and joint manipulation help reduce chronic pain and inflammation‚ improving mobility and function. IMT also supports rehabilitation by enhancing circulation and reducing muscle tension‚ which is particularly beneficial for conditions like arthritis and fibromyalgia. By addressing the root causes of chronic pain and dysfunction‚ IMT provides a holistic approach to managing chronic illnesses‚ improving quality of life and supporting overall wellness;
Case Studies and Success Stories
Real-life examples highlight the effectiveness of Integrated Manual Therapy in treating chronic pain‚ improving mobility‚ and enhancing overall function. Success stories demonstrate its transformative impact on patients with complex conditions‚ showcasing measurable outcomes and improved quality of life through tailored treatment plans.
6.1 Patient Outcomes and Testimonials
Patient testimonials highlight the transformative impact of Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT). Many report significant pain reduction‚ improved mobility‚ and enhanced overall well-being. Testimonials often emphasize how IMT addressed chronic conditions‚ such as lower back pain or limited joint movement‚ where other treatments fell short. Patients praise the personalized approach‚ noting how tailored sessions led to sustained recovery and improved quality of life. One patient shared‚ “IMT changed my life‚ allowing me to return to activities I thought were lost forever.” These outcomes underscore IMT’s effectiveness in restoring function and promoting long-term wellness.
6.2 Real-World Applications and Results
Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) has shown remarkable results in clinical and real-world settings‚ addressing diverse conditions like chronic pain‚ sports injuries‚ and post-surgical recovery. Case studies reveal its effectiveness in improving mobility and reducing discomfort for patients with complex musculoskeletal issues. For example‚ athletes with recurring injuries report faster recovery times‚ while individuals with chronic pain experience sustained relief. The therapy’s adaptability to various patient needs makes it a versatile tool in modern healthcare‚ often used alongside other treatments for enhanced outcomes. These practical applications highlight IMT’s role in achieving measurable‚ long-term results.
6.3 Common Conditions Treated
Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) is widely used to address a variety of musculoskeletal and neurological conditions. Commonly treated conditions include chronic pain‚ sports injuries‚ sciatica‚ fibromyalgia‚ and postural dysfunction.
Therapists also treat repetitive strain injuries‚ such as carpal tunnel syndrome‚ and degenerative joint conditions like osteoarthritis. By targeting soft tissue‚ joints‚ and the nervous system‚ IMT helps restore movement and reduce discomfort‚ making it an effective treatment for both acute and chronic issues.
Comparison with Other Therapeutic Modalities
Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) differs from techniques like acupuncture or yoga by focusing on hands-on‚ evidence-based methods to restore mobility and reduce pain‚ emphasizing a holistic approach.
7.1 vs. Physical Therapy
Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) and physical therapy share goals like pain relief and improved mobility but differ in approach. IMT emphasizes hands-on techniques‚ such as soft tissue mobilization and joint manipulation‚ focusing on the body’s interconnected systems. Physical therapy often incorporates exercises‚ modalities like heat or ultrasound‚ and mechanical devices. While physical therapy may focus on specific injuries or conditions‚ IMT adopts a more holistic‚ patient-centered approach‚ addressing the entire body to restore function and promote lasting wellness. Both modalities aim to enhance movement but vary in methodology and scope.
7.2 vs. Chiropractic Care
Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) and chiropractic care both aim to improve mobility and reduce pain but differ in approach. Chiropractic care primarily focuses on spinal adjustments to align the vertebrae and relieve pressure on the nervous system. In contrast‚ IMT incorporates a broader range of techniques‚ including soft tissue mobilization‚ joint mobilization‚ and neuromuscular methods. While chiropractic care is often more localized‚ IMT adopts a holistic approach‚ addressing the entire body to restore balance and function. Both modalities emphasize manual techniques but vary in scope and methodology.
7.3 vs. Osteopathic Manipulation
Osteopathic manipulation and Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) share similarities in their hands-on approaches to improving mobility and reducing pain. Osteopathic manipulation emphasizes the interrelationship of the body’s systems‚ focusing on the musculoskeletal framework to enhance overall health. IMT‚ while also manual‚ integrates a wider array of techniques‚ including soft tissue work and neuromuscular methods. Both modalities prioritize patient-centered care but differ in their foundational philosophies and techniques. IMT often incorporates evidence-based practices‚ whereas osteopathic manipulation is deeply rooted in osteopathic principles‚ making each approach unique yet complementary in therapeutic outcomes.
7.4 vs. Massage Therapy
Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) and massage therapy share the goal of relieving tension and improving mobility but differ in scope and technique. Massage therapy focuses primarily on soft tissue manipulation‚ targeting muscles and connective tissue to reduce stress and pain. IMT‚ however‚ incorporates a broader range of methods‚ including joint mobilization and neuromuscular techniques‚ to address complex musculoskeletal issues. While massage offers relaxation and localized relief‚ IMT aims for comprehensive‚ long-term functional recovery‚ making it a more holistic approach for chronic or deep-seated conditions.

Ethical Considerations and Professional Standards
Integrated Manual Therapy requires adherence to strict ethical standards‚ including patient confidentiality‚ informed consent‚ and maintaining professional boundaries. Practitioners must stay within their scope of practice and demonstrate cultural sensitivity to ensure trust and effective care.
8.1 Patient Confidentiality and Informed Consent
Patient confidentiality is a cornerstone of Integrated Manual Therapy‚ ensuring all personal and medical information remains protected. Informed consent is essential‚ requiring clear communication of treatment benefits‚ risks‚ and alternatives. Therapists must obtain explicit patient agreement before proceeding‚ respecting autonomy and fostering trust. This ethical practice upholds legal standards and builds a collaborative therapeutic relationship‚ ensuring patients are fully informed and actively involved in their care.

8.2 Scope of Practice and Legal Boundaries
Integrated Manual Therapists must adhere to a defined scope of practice‚ ensuring treatments align with their training and certification. Legal boundaries require therapists to operate within their licensed expertise‚ avoiding practices outside their professional jurisdiction. This includes refraining from medical diagnoses unless properly licensed and not overstepping into other healthcare professionals’ roles. Compliance with state laws and professional standards is essential to maintain ethical practice and avoid legal repercussions‚ ensuring safe and effective care for patients. Adhering to these guidelines fosters trust and upholds the integrity of the therapy profession.
8.3 Cultural Competence and Sensitivity
Integrated Manual Therapists must demonstrate cultural competence and sensitivity to effectively treat diverse patient populations. Therapists should be aware of their own biases and adapt their communication and treatment approaches to respect patients’ cultural backgrounds‚ beliefs‚ and values. This includes being sensitive to differences in pain perception‚ body language‚ and healthcare expectations. By fostering an inclusive and nonjudgmental environment‚ therapists can build trust and ensure equitable care. Cultural sensitivity also involves staying informed about diverse healthcare practices and tailoring interventions to meet individual needs while respecting patient preferences and beliefs.
The Future of Integrated Manual Therapy
The future of Integrated Manual Therapy looks promising‚ with advancements in research‚ technology‚ and evidence-based techniques. Expect increased integration with other healthcare fields and a focus on patient-centered care.
9.1 Emerging Trends and Innovations
Emerging trends in Integrated Manual Therapy include advancements in evidence-based techniques‚ personalized treatment plans‚ and the integration of technology. Innovations like AI-driven diagnostic tools and wearable devices are enhancing precision and patient outcomes. Additionally‚ the rise of telehealth platforms is expanding access to manual therapy services remotely. These advancements are reshaping the field‚ enabling therapists to deliver more targeted and effective care. The focus remains on holistic‚ patient-centered approaches‚ ensuring IMT continues to evolve as a dynamic and impactful therapeutic modality.
9.2 Advancements in Research and Evidence-Based Practice
Research in Integrated Manual Therapy is advancing rapidly‚ with a focus on evidence-based practices to enhance treatment outcomes. Systematic reviews and clinical studies are identifying optimal techniques for pain management and functional improvement. New tools‚ such as biomechanical analysis software‚ are aiding therapists in personalized care. Collaboration between researchers and practitioners ensures that findings are translated into effective clinical applications. This commitment to scientific rigor is elevating IMT’s role in modern healthcare‚ making it a trusted modality for addressing diverse musculoskeletal and neurological conditions;
9.3 Expanding Applications and Integration with Other Disciplines
Integrated Manual Therapy is increasingly being applied in diverse clinical settings‚ from sports medicine to chronic pain management. Its principles are being integrated with physical therapy‚ chiropractic care‚ and occupational therapy to enhance patient outcomes. This interdisciplinary approach fosters a more comprehensive understanding of movement and function. By collaborating with other healthcare fields‚ IMT is expanding its reach‚ offering innovative solutions for complex conditions. This integration not only broadens its applications but also strengthens its role in addressing modern healthcare challenges.
Integrated Manual Therapy is a transformative‚ evidence-based approach that restores function and promotes wellness. Its patient-centered‚ holistic methodology makes it invaluable in modern healthcare‚ ensuring optimal outcomes.
10.1 Recap of Key Points
Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) is a holistic‚ evidence-based practice combining soft tissue mobilization‚ joint manipulation‚ and neuromuscular techniques. It focuses on restoring function‚ relieving pain‚ and improving mobility. IMT emphasizes a patient-centered approach‚ addressing the whole body to promote healing and long-term wellness. By integrating diverse manual therapies‚ it offers personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs. This approach collaborates with other healthcare modalities‚ ensuring comprehensive care. The therapy’s effectiveness lies in its ability to adapt to various conditions‚ making it a valuable tool in modern healthcare.
10.2 The Importance of Integrated Manual Therapy in Modern Healthcare
Integrated Manual Therapy (IMT) plays a vital role in modern healthcare by offering a comprehensive‚ non-invasive approach to treating musculoskeletal and chronic conditions. Its emphasis on restoring function‚ reducing pain‚ and enhancing mobility makes it a valuable tool for patients seeking holistic care; IMT’s adaptability to diverse conditions‚ combined with its focus on evidence-based practices‚ ensures effective outcomes. By addressing the whole body‚ it complements traditional treatments‚ providing a cost-effective and patient-centered solution. This makes IMT a cornerstone in contemporary healthcare‚ promoting long-term wellness and improving quality of life for individuals worldwide.

